Please email me at:
Or use the form below.
[contact-form 1 “Contact form 1”]
The no-pants guide to spending, saving, and thriving in the real world.
Today, I am starting a series, Money Problems: 30 Days to Perfect Finances. The series will consist of 30 things you can do in one setting to perfect your finances. It’s not a system to magically make your debt disappear. Instead, it is a path to understanding where you are, where you want to be, and–most importantly–how to bridge the gap.
I’m not going to run the series in 30 consecutive days. That’s not my schedule. Also, I think that talking about the same thing for 30 days straight will bore both of us. Instead, it will run roughly once a week. To make sure you don’t miss a post, please take a moment to subscribe, either by email or rss.
In this, the first installment, we’re going to talk about goals.
First, we’re going to ask 3 questions.
The first question is “What is your goal?” Of course, in this series, on this site, we’re only going to be addressing your financial goals. Losing 300 pounds, growing wings, and flying to the moon may be an admirable goal, but it’s considerably outside of the scope of this project.
So, what is your financial goal? Do you want to retire a millionaire, or become financially independent? Do you want to pay off your debt, or save enough money to see the world? Do you want to learn how to retire by 40?
Your goal does not matter…to anyone but you. To you, though, it is terribly important. Without a goal, how can you measure you progress and see what you have accomplished? It’s easy to get frustrated and give up when you can’t look back and see what successes you have actually accumulated.
Whatever your goal, you have to do two things:
The second major question to ask yourself is “Why?” Why is this goal important to you? Why do you care?
If you can’t answer that, it’s time to sit back and think about it for a while. Without a solid reason to succeed, you’ll lose motivation and fail. Are you getting out of debt to give yourself a secure retirement? Do you want to save to travel the world because you’ve been dreaming about it since you were in diapers? Do you simply want to provide a secure future for your family? Whatever your reason, it is–and should be–uniquely yours.
The third and final question is “How can you make it happen?” That question has an extremely simple answer: read the rest of the series.
Today, I am continuing the series, Money Problems: 30 Days to Perfect Finances. The series will consist of 30 things you can do in one setting to perfect your finances. It’s not a system to magically make your debt disappear. Instead, it is a path to understanding where you are, where you want to be, and–most importantly–how to bridge the gap.
I’m not running the series in 30 consecutive days. That’s not my schedule. Also, I think that talking about the same thing for 30 days straight will bore both of us. Instead, it will run roughly once a week. To make sure you don’t miss a post, please take a moment to subscribe, either by email or rss.
On this, Day 6, we’re going to talk about cutting your expenses.
Once you free up some income, you’ll get a lot of leeway in how you’re able to spend your money, but also important–possibly more important–is to cut out the crap you just don’t need. Eliminate the expenses that aren’t providing any value in your life. What you need to do is take a look at every individual piece of your budget, every line item, every expense you have and see what you can cut. Some of it, you really don’t need. Do you need a paid subscription to AmishDatingConnect.com?
If you need to keep an expense, you can just try to lower it. For example, cable companies regularly have promotions for new customers that will lower the cost to $19 a month for high-speed internet. Now, if you call up the cable company and ask for the retention department, tell them you are going to switch to a dish. Ask, “What are you willing to do to keep my business?” There is an incredibly good chance that they will offer you the same deal–$20 a month–for the next three or four months. Poof, you save money. You can call every bill you’ve got to ask them how you can save money.
I called my electric company and my gas company to get on their budget plans. This doesn’t actually save me money but it does provide me with a consistent budget all year long, so instead of getting a $300 gas bill in the depths of January’s hellish cold, I pay $60 a month. It is averaged out over the course of the year. It feels like less and it lets me get a stable budget. Other bills are similar. You can call your credit card companies and tell them everything you take your business to another card that gave you an offer of 5% under what ever you are currently paying. It doesn’t even have to be a real offer. Just call them up and say you are going to transfer your balance away unless they can meet or beat the new interest rate. If you’ve been making on-time payments for any length of time–even six months or a year–they’re going to lower the interest rate business, no problem. Start out by asking for at least a 5% drop. In fact, demand no more than 9.9%.
Once you’ve gone through every single one of your bills, you’ll be surprised by how much money you’re no longer paying, whether it’s because somebody lowered the bill for you or you scratched it off the list completely.
When you’re setting up a niche site, you need to monetize it. You need to have a way to make money, or it’s a waste of time.
There are two main ways to do that: AdSense or product promotion. To set up an AdSense site, you write a bunch of articles, post them on a website with some Google ads, and wait for the money to roll in.
I don’t do that.
I don’t own a single AdSense site and have never set one up. This article is not about setting up an Adsense site.
My niches site are all product-promotion sites. I pick a product–generally an e-book or video course–and set up a site dedicated to it.
Naturally, picking a good product is an important part of the equation.
The most important part of product selection is that the product has an affiliate program. Without that, there’s no money to be made. There are a lot of places to find affiliate programs. Here are a few:
The first thing you need to do is sign up for whichever program you intend to use.
If you’re not going with Clickbank, feel free to skip ahead to the section on keyword research.
Once you are signed up and logged in, click on the “Marketplace” link at the top of the screen.
From here, it’s just a matter of finding a good product to sell. Here are the niches we’re going to be looking for:
I’m going to look for one or two good products in each niche. When that’s done we’ll narrow it down by consumer demand.
For now, go to advanced search.
Enter your keyword, pick the category and set the advanced search stats. Gravity is the number of affiliates who have made sales in the last month. I don’t like super-high numbers, but I also want to make sure that the item is sellable. Over 10 and under 50 or so seems to be a good balance.
The average sale just ensures that I’ll make a decent amount of money when someone buys the product. I usually aim for $25 or more in commissions per sale. Also, further down, check the affiliate tools box. That means the seller will have some resources for you to use.
This combination will give us 36 products to check out for back pain, unfortunately, none of the results are for back pain products. After unchecking the affiliate tools and setting the gravity to greater than 1, I’ve got 211 results. Sorting by keyword relevance, I see three products, two of which look like something I’d be interested in promoting. One has a 45% commission, the other is 55%. The X-Pain Method has an initial commission of $34 and claims a 5% refund rate. Back Pain, Sciatica, and Bulging Disc Relief pays $16, which will make it a potentially easier sale. I’ll add both to the list for further research.
I’m not going to detail the search for the rest of the niches. That would be repetitive. You can see my selections here:
Now we’re going to go through a few steps for each of these products.
We need to make sure the sales page doesn’t suck. If the site doesn’t work, is hard to read or navigate, has a hard-to-find order button, or just doesn’t look professional, it’s getting cut.
If it has an email subscription form, we’ll need to subscribe, then double-check to make sure our affiliate information isn’t getting dropped in the emails. If it is, the seller is effectively stealing commissions. In the interest of time and laziness, I’m going to eliminate anyone pushing for an email subscription. It’s harder–and time-consuming–to monitor that. On of my niche site had a seller completely drop their product. Instead, they pushed for email subscriptions so they could promote other products as an affiliate. Absolutely unethical.
Finally, we’re going to visit the checkout page. You need to do this from every links in the newsletter and the links on the sales page, just to make sure you’ll get your money.
The way to tell who’s being credited is to look at the bottom of the order page, under the payment information. It should say [affiliate = xxx] where xxxis your ClickBank ID. Anything else, and the product gets cut from the list.
When you are checking these, don’t click on every possible link at once. That confuses the cookies. Do one at a time. I tried to do it in one batch for this post and lost half of the cookies. If it weren’t for the fact that I already own one of the products and bought it through my own link and got credited, I would have been talking undeserved trash about thieving companies.
Sometimes, when you’re examining a product, it just doesn’t feel right. When that happens, drop it. There are millions of other products you can promote. In this case, I’m dropping the anger management program because, in my experience, angry people don’t think they are the problem. Here’s a life tip: If everyone else is a jerk, the problem probably isn’t everyone else.
Now we’re down to 10 products in 6 niches. At this point, we’re comfortable with the sales pages and we know that they are crediting commissions. As it stands right now, all of the products are worth promoting.
We’ll make the final determination after doing some heavy keyword research in the next installment. That’s where we’ll find out how hard it is to compete.
Any questions?
Today, I am continuing the series, Money Problems: 30 Days to Perfect Finances. The series will consist of 30 things you can do in one setting to perfect your finances. It’s not a system to magically make your debt disappear. Instead, it is a path to understanding where you are, where you want to be, and–most importantly–how to bridge the gap.
I’m not running the series in 30 consecutive days. That’s not my schedule. Also, I think that talking about the same thing for 30 days straight will bore both of us. Instead, it will run roughly once a week. To make sure you don’t miss a post, please take a moment to subscribe, either by email or rss.
On this, Day 9, we’re going to talk about health insurance.
The first thing to understand is that there is a difference between health care and health insurance. Health care is what the doctors do. Health insurance is when the insurance companies pay for it. Or don’t. They are not the same thing. I won’t be addressing who should get care or who should be paying for insurance. That’s political and I try to avoid that here.
I won’t spend much time discussing health care as a “right”. It’s not. If a right requires somebody to actively do something for you, it’s not a right. It can’t be. The logical conclusion of requiring somebody to provide you care gets to be a intellectual exercise to be completed elsewhere. That, too, is political.
What I will discuss are the components of a health insurance plan is the U.S. and what to watch out for when planning your insurance coverage.
This is the amount you pay for your health insurance. For people with employer-sponsored insurance, this is usually paid out of each paycheck, deducted pre-tax. For those with an individual plan, it’s almost always a monthly payment. There generally isn’t much you can do to lower this much. Most employers offer, at most, 2-3 options, ranging from a good plan for a high premium to “we’ll mail you leeches if we think you’re dying” for a much smaller price.
This is a flat fee paid out of pocket when you get medical care. Depending on your plan and the type of visit, this could be $10-50 or higher. For example, with a plan I participated in recently, the copay was $15 for an office visit, $25 for urgent care, and $100 for an emergency room visit. The office visit and urgent care visit were billed the same amount to the insurance company, so the price difference was entirely arbitrary. Currently, all health insurance plans are required to pay preventative care visits at 100%, meaning there is no copay.
This is the payment split between the insurance company and the insured. 80/20 is a common split for plans with coinsurance. That means the insurance company will pay just 80% of the bill, until the insured has paid the entire out-of-pocket maximum. After that, the coverage is 100%.
This is the amount that an insurance company won’t pay. It has to be covered by the insured before the insurance company does anything. For example, if you have an insurance plan with a $25 copay, 80/20 coinsurance and a $100 deductible, and paying for an office visit costing $600 would look something like this: $25 for the copay, followed by $75 to max out the copay, leaving $500 to be split 80/20 or $400 paid by the insurance company and $100 paid by the insured. That office visit would cost $200 out-of-pocket. The next identical visit would be cheaper because the deductible is annual and doesn’t get paid per incident. That one would cost $115 out of pocket.
Health Savings Account. For people with a high-deductible plan–that is, a plan with a deductible of at least $1200 in 2011–they are eligible to open an HSA. This is a savings account dedicated to paying medical expenses, excluding OTC medication. It can be used for vision, dental, or medical care. Payroll contributions are taken pre-tax, which makes it a more affordable way to afford major medical expenses. Unfortunately, there are annual contribution limits. Currently $3050 for an individual account and $6150 for a family account. HSAs do not expire, so you can contribute now, and save the money for medical expenses after retirement.
Flexible Spending Account. This is similar to an HSA, but the contributed funds evaporate at the end of the year. It’s “use it or you’re screwed” plan.
If you’re not getting health insurance through your employer or another group, you are on an individual plan. These cost more because they A) don’t benefit from the economy of scale presented by getting 50 or 100 or 1000 people on the same plan, and B) you don’t have an employer subsidizing your premium.
If your employer provides health insurance, you have an employer-sponsored plan. Possibly the fastest way to correct problems with the health insurance industry would be to make individual plan premiums tax-deductible, while eliminating that deduction for employers and letting insurance companies work across state lines. That would eliminate the mutated pseudo-market we have right now, and force the insurance companies to compete for your business. Honest competition is the most sure way to increase efficiency and service while reducing costs. It beats “one payer” or “socialized” care which add overhead to the process and hide the premiums in increased taxes.
Most employer-sponsored plans only allow you to make changes at a specific time of the year, unless you have a “life changing event”, like marriage, divorce, death, or children.
After you use your health insurance, the company will send an EOB, showing you what was billed, what they paid, and what you’ll be responsible for. It’s fascinating to see the difference between what gets billed by the doctor and what the insurance company is willing to pay, by contract. You should read this, to at least understand what you are consuming and how much is getting paid for you.
If your insured care cost more than your maximum dollar limit, or maximum annual limit, the insurance company stops paying. this was supposed to be going away under the Patient Protection and Affordable Care Fraud Act. Unfortunately, if an insurance company offers a crap plan, they have been allowed to apply for waivers based on the fact that they offer a crap plan. The deciding factor in whether the waiver is granted seems to be the amount of the political contributions the insurance company has made to the correct political entities, but maybe I’m just bitter.
This is the most you will have to pay directly with coinsurance. After you pay this amount, the insurance company will cover 100% of expenses, subject to the maximum limit.
The Consolidated Omnibus Budget Reconciliation Act of 1985 is, in short, an opportunity to continue your employer-sponsored health plan–minus the subsidy–after you have left the employer. It’s expensive, but it keeps you covered, and will eliminate issue with pre-existing conditions when you get a new plan.
This is an extremely-high-deductible plan, typically $10,000 or more. For the people who can’t afford coverage, this is insurance-treated-as-insurance. It’s coverage when you absolutely need it, not when you feel a bit ill. $10,000 isn’t a bankruptcy-level bill, while $100,000 usually is. This plan prevent medical bankruptcy for a small monthly fee. For the people who got screwed by a PPAACFA waiver, it bridges the gap between a plan that’s useful for minor things and protection when something goes really wrong.
Now that we’ve looked at the terms you need to understand, we’re going to talk about some things to check before deciding what coverage is right for you.
Do you need coverage for yourself, or yourself and your family? If you and your spouse are both working, make sure to run the math for every possible combination that will cover everyone. Is it cheaper to have one of you cover yourself and the kids, while the other just gets an individual plan?
It’s really easy to blow through a $3000 annual maximum. If you’ve got a low annual max, look into a supplemental catastrophic plan.
For years, my wife paid for insurance that covered herself and the kids, while I covered myself. When we were expecting brat #3, I added her to my insurance plan, without having her cancel hers. When the bill came, my insurance plan covered the coinsurance and deductible, which saved us thousands of dollars when the baby was born.
If you’ve got a pre-existing condition, it can be difficult to get insurance if you don’t already have coverage. This makes sense. It prevents someone from corrupting the idea of insurance by waiting until something goes really wrong before getting a plan. Without this, all of the insurance companies would be bankrupt in a year. This is one of the biggest benefits of COBRA. It’s a short-term bridge plan that eliminates the idea of a pre-exisiting condition deadbeat. If you’ve got insurance, you can transfer to a different plan. If you don’t, you can’t.
Your homework today is to get a copy of the details of your health insurance and look up all of the above terms and situations. How well are you covered? Did anything surprise you?
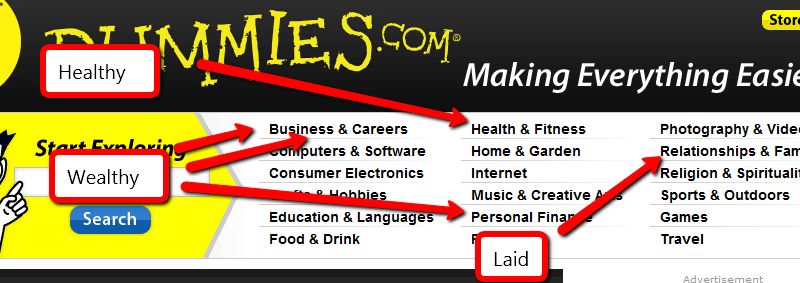
If you want to make money, help someone get healthy, wealthy or laid.
This section was quick.
Seriously, those three topics have been making people rich since the invention of rich. Knowing that isn’t enough. If you want to make some money in the health niche, are you going to help people lose weight, add muscle, relieve stress, or reduce the symptoms of some unpleasant medical condition? Those are called “sub-niches”. (Side question: Viagra is a sub-niche of which topic?)
Still not enough.
If you’re going to offer a product to help lose weight, does it revolve around diet, exercise, or both? For medical conditions, is it a way to soothe eczema, instructions for a diabetic diet, a cure for boils, or help with acne? Those are micro-niches.
That’s where you want to be. The “make money” niche is far too broad for anyone to effectively compete. The “make money online” sub-niche is still crazy. When you get to the “make money buying and selling websites” micro-niche, you’re in a territory that leaves room for competition, without costing thousands of dollars to get involved.
Remember that: The more narrowly you define your niche market, the easier it is to compete. You can take that too far. The “lose weight by eating nothing but onions, alfalfa, and imitation caramel sauce” micro-niche is probably too narrowly defined to have a market worth pursuing. You need a micro-niche with buyers, preferably a lot of them.
Now the hard part.
How do you find a niche with a lot of potential customers? Big companies pay millions of dollars every year to do that kind of market research.
Naturally, I recommend you spend millions of dollars on market research.
No?
Here’s the part where I make this entire series worth every penny you’ve paid. Times 10.
Steal the research.
My favorite source of niche market research to steal is http://www.dummies.com/. Click the link and notice all of the wonderful niches at the top of the page. Jon Wiley & Sons, Inc. spends millions of dollars to know what topics will be good sellers. They’ve been doing this a long time. Trust their work.
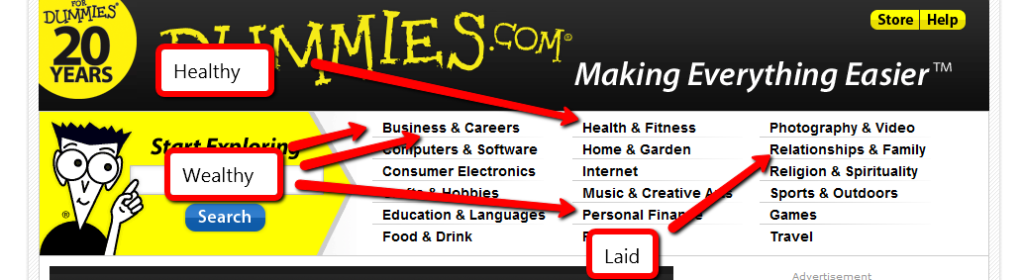
You don’t have to concentrate on the topics I’ve helpfully highlighted, but they will make it easier for you. Other niches can be profitable, too.
Golf is a great example. Golfers spend money to play the game. You don’t become a golfer without having some discretionary money to spend on it. I’d recommend against consumer electronics. There is a lot of competition for anything popular, and most of that is available for free. If you choose to promote some high-end gear using your Amazon affiliate link, you’re still only looking at a 3% commission.
I like to stick to topics that people “need” an answer for, and can find that answer in ebook form, since I will be promoting a specific product.
With that in mind, pick a topic, then click one of the links to the actual titles for sale. The “best selling titles” links are a gold mine. You can jump straight to the dummies store, if you’d like.
Of the topics above, here’s how I would narrow it down:
1. Business and Careers. The bestsellers here are Quickbooks and home buying. I’m not interested in either topic, so I’ll go into “More titles”. Here, the “urgent” niches look like job hunting and dealing with horrible coworkers. I’m also going to throw “writing copy” into the list because it’s something I have a hard time with.
2. Health and Fitness. My first thought was to do a site on diabetic cooking, but the cooking niche is too competitive. Childhood obesity, detox diets and back pain remedies strike me as worth pursuing. I’m leaning towards back pain, because I have a bad back. When you’ve thrown your back out, you’ve got nothing to do but lie on the couch and look for ways to make the pain stop. That’s urgency.
3. Personal Finance. The topics that look like good bets are foreclosures and bankruptcies. These are topics that can cost thousands of dollars if you get them wrong. I hate to promote a bankruptcy, but some people are out of choices. Foreclosure defense seems like a good choice. Losing your home comes with a sense of urgency, and helping people stay in their home makes me feel good.
4. Relationships and Family. Of these topics, divorce is probably a good seller. Dating advice definitely is. I’m not going to detail either one of those niches here. Divorce is depressing and sex, while fun, isn’t a topic I’m going to get into here. I try to be family friendly, most of the time. Weddings are great topic. Brides are planning to spend money and there’s no shortage of resources to promote.
So, the niches I’ve chosen are:
I won’t be building 9 niche sites in this series. From here, I’m going to explore effective keywords/search terms and good products to support. There’s no guarantee I’ll find a good product with an affiliate program for a niche I’ve chosen that has keywords that are both highly searched and low competition, so I’m giving myself alternatives.
For those of you following along at home, take some time to find 5-10 niches you’d be willing to promote.
The important things to consider are:
1. Does it make me feel dirty to promote it?
2. Will there be customers willing to spend money on it?
3. Will those customers have an urgent need to solve a problem?
I’ve built sites that ignore #3, and they don’t perform nearly as well as those that consider it. When I do niche sites, I promote a specific product. It’s pure affiliate marketing, so customers willing to spend money are necessarily my target audience.